Top Cybersecurity Best Practices for Businesses in 2026
A practical 10-point roadmap for building resilient cybersecurity in 2026: culture, IAM, layered defenses, monitoring, cloud security, compliance, and expert support.
Executive Summary
In 2026, cybersecurity is no longer confined to IT; it is a boardroom priority. As organizations accelerate digital transformation, risks from data breaches, ransomware, and operational disruption continue to rise. Hybrid work, cloud platforms, and interconnected systems demand a more mature and strategic security approach than ever before.
Implementing resilient cybersecurity solutions for business enables organizations to safeguard sensitive data, maintain continuity, and preserve stakeholder trust. Done well, cybersecurity also supports business growth by minimizing downtime, protecting brand reputation, and improving compliance readiness.
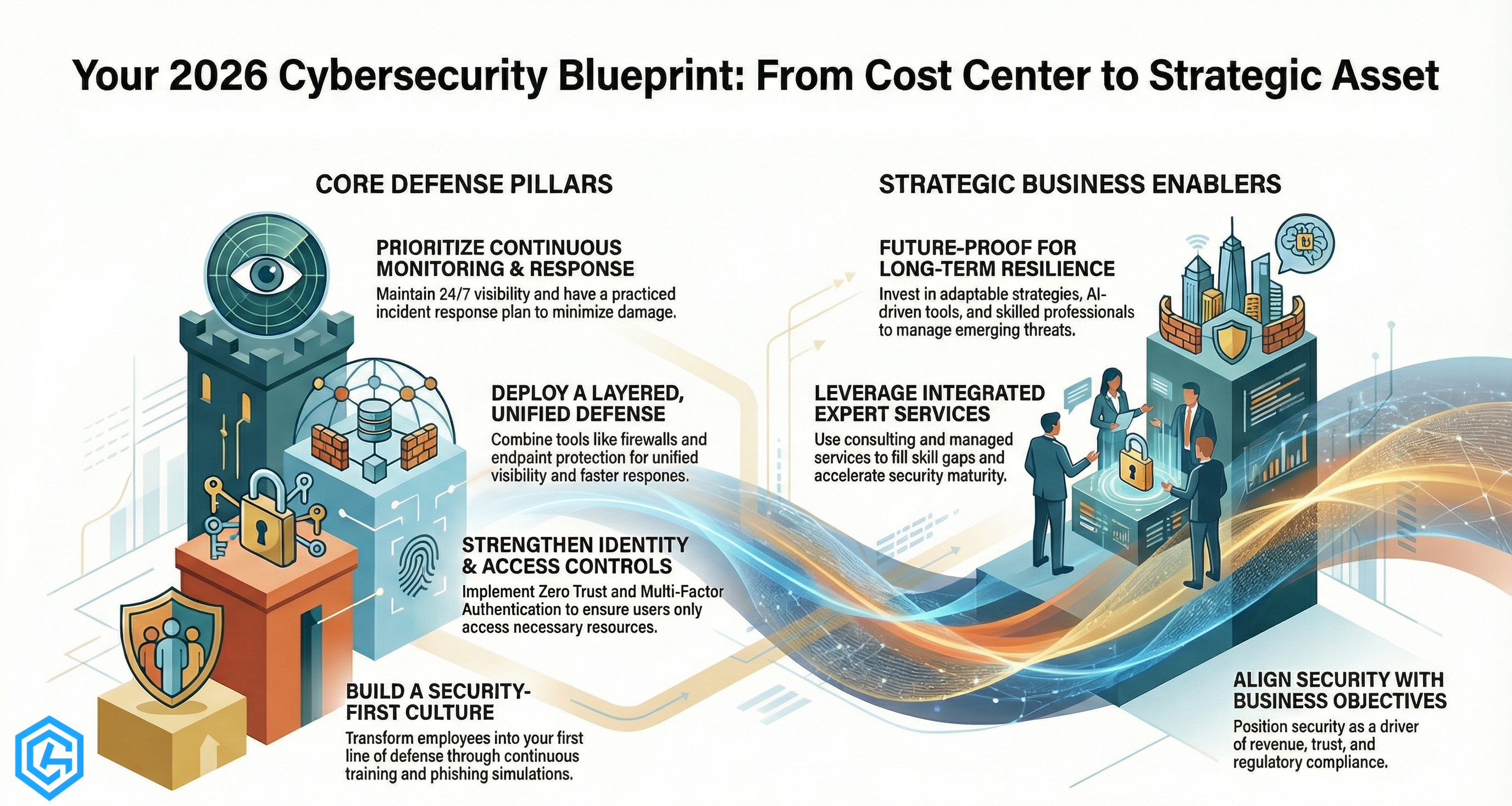
Top 10 Cybersecurity Best Practices for Business in 2026
1) Establish a Security-First Business Culture
Cybersecurity depends on people. Employees are the first line of defense and are frequently the most common point of failure (Inc., 2024). In 2026, organizations must move beyond one-time awareness sessions and integrate cybersecurity into daily workflows.
Ongoing education, simulated phishing exercises, and clear internal policies help employees recognize threats and respond responsibly. For example, after implementing regular phishing simulations, many organizations see measurable reductions in unsafe clicks and faster reporting of suspicious emails.
2) Strengthen Identity and Access Management (IAM) Controls
Effective IAM ensures that users access only the resources necessary for their roles, minimizing unnecessary exposure. Introducing multi-factor authentication and running access audits are strong first steps (Gartner, 2024).
Best practices also include:
- Least-privilege access
- Regular credential and entitlement reviews
- Role-based permissions (RBAC)
- Zero Trust approaches that continuously authenticate and authorize users across locations and devices
3) Implement Layered Security Architecture
No single tool can defend against all threats. A layered defense combines endpoint protection, firewalls, intrusion detection, secure configurations, and segmentation to reduce attack success.
Integration matters: disconnected tools create blind spots, while unified visibility enables faster detection and response. At this stage of maturity, cybersecurity solutions for business must evolve alongside operational complexity.
4) Prioritize Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
Threats do not operate on a schedule, and neither should security monitoring. Continuous visibility across networks, endpoints, identity, and cloud platforms helps detect suspicious behavior early.
Equally important is a documented incident response plan. Organizations that practice breach scenarios respond faster, limit damage, and recover more efficiently.
5) Secure Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Cloud adoption has accelerated, but misconfigurations remain a leading cause of breaches. Businesses should clearly operationalize shared responsibility models.
Core cloud security practices include:
- Encryption for data in transit and at rest
- Continuous configuration monitoring
- Access audits and periodic privilege cleanup
- Workload protection aligned to the cloud provider
Cloud security should be proactive, aligning governance with scalability and performance goals.
Talk to Cyberaube about strengthening your 2026 security roadmap
6) Align Cybersecurity with Business Objectives
Security initiatives succeed when they support business growth. Leaders should communicate cybersecurity investments in terms of risk reduction, uptime protection, and customer trust.
When executives understand how cybersecurity solutions and services contribute to revenue stability and compliance, security becomes a strategic enabler rather than a cost center.
7) Leverage Expert Guidance and Specialized Support
As threats grow more complex, internal teams may face skill gaps. Engaging cyber security consulting services can provide specialized expertise for risk assessments, architecture design, and compliance alignment.
External specialists also bring objective perspective and proven methodologies, helping organizations accelerate maturity without overburdening internal resources.
8) Adopt an Integrated Security Services Model
Fragmented security efforts create inefficiencies and vulnerabilities. A unified services approach—combining staffing solutions, managed support services, professional services, and cybersecurity consultation—delivers end-to-end protection across the security lifecycle.
With managed services and implementation expertise spanning 20+ enterprise security platforms, CyberAube Technologies supports diverse needs including cybersecurity staffing, managed SIEM operations, and IAM implementation.
9) Prepare for Regulatory and Compliance Evolution
Regulatory expectations continue to expand globally. Organizations must demonstrate accountability through documented controls, audits, and risk management processes.
Compliance should strengthen security posture rather than exist in isolation. When aligned correctly, regulatory frameworks reinforce operational discipline and long-term resilience.
10) Future-Proof Cybersecurity for Long-Term Resilience
Cybersecurity is not static. AI, behavioral analytics, and automated response are shaping the next generation of defense. However, tools alone are insufficient without skilled professionals and strong governance.
Organizations that invest early in adaptable strategies, workforce development, and scalable architectures are better positioned to manage uncertainty. As digital ecosystems grow more complex, cybersecurity solutions for business remain foundational to sustainable growth and stakeholder trust.
FAQ
Why are numbered best practices important for cybersecurity planning?
They provide a structured roadmap, making complex security strategies easier to prioritize and implement.
How often should businesses reassess their cybersecurity posture?
Continuously, with formal reviews conducted annually or after major system changes.
Is external cybersecurity expertise necessary for growing organizations?
Yes. Specialized expertise accelerates maturity and fills critical skill gaps efficiently.
Can cybersecurity scale with business growth?
Yes. When built on flexible frameworks, security can evolve alongside organizational expansion without disruption.
How do cyberattacks typically impact business operations?
Cyberattacks can cause downtime, data loss, financial damage, and reputational harm. Even short disruptions can affect customer trust and regulatory compliance.
What role does leadership play in cybersecurity preparedness?
Leadership sets priorities, allocates budgets, and drives accountability. Active executive support improves consistency and follow-through.
Are managed security services suitable for mid-sized businesses?
Yes. Managed services help mid-sized organizations access advanced capabilities without the cost of building large in-house teams.
How can businesses measure cybersecurity effectiveness?
Use a mix of reduced incident frequency, response times, audit outcomes, compliance scores, and regular risk assessments.
What is the biggest cybersecurity mistake businesses still make?
Relying on outdated tools or assuming basic defenses are sufficient. Threats evolve constantly, and static security approaches quickly become ineffective.
How should businesses prepare for emerging cyber threats beyond 2026?
Invest in continuous learning, scalable security architectures, skilled professionals, and regularly updated policies and response plans.
Ready to Strengthen Your Cybersecurity Posture?
CyberAube Technologies helps organizations build resilient security programs with expert-led strategy and integrated protection.